Pandas中的pivot()函数根据列值重塑数据。它以简单的列式数据作为输入,并将条目分组为二维表。
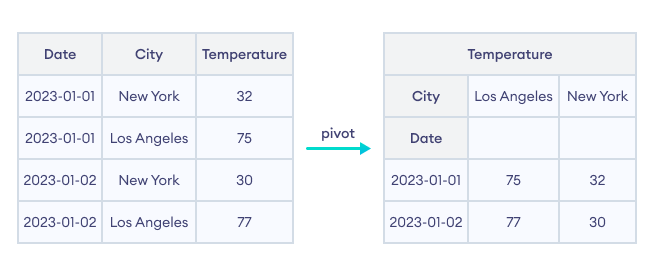
让我们看一个例子。
import pandas as pd
# create a dataframe
data = {'Date': ['2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02'],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles'],
'Temperature': [32, 75, 30, 77]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print("Original DataFrame\n", df)
print()
# pivot the dataframe
pivot_df = df.pivot(index='Date', columns='City', values='Temperature')
print("Reshaped DataFrame\n", pivot_df)输出
Original DataFrame
Date City Temperature
0 2023-01-01 New York 32
1 2023-01-01 Los Angeles 75
2 2023-01-02 New York 30
3 2023-01-02 Los Angeles 77
Reshaped DataFrame
City Los Angeles New York
Date
2023-01-01 75 32
2023-01-02 77 30
在此示例中,我们使用pivot()来重塑DataFrame df。Date列被设置为index,City被设置为列,Temperature被设置为值。
请注意输出部分中的原始DataFrame和重塑后的DataFrame。重塑后的DataFrame是一个多维表,根据城市和日期显示温度。
因此,pivot()操作重塑数据,使其在进一步分析时更加清晰。
pivot()语法
Pandas中pivot()的语法是
df.pivot(index=None, columns=None, values=None)这里,
index:用作行标签的列columns:将被重塑为列的列values:用于新DataFrame值的列
示例:多个值的pivot()
如果我们省略pivot()中的values参数,它将选择所有剩余的列(除了指定的index和columns之外)作为透视表的值。
让我们看一个例子。
import pandas as pd
# create a dataframe
data = {'Date': ['2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02'],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles'],
'Temperature': [32, 75, 30, 77],
'Humidity': [80, 10, 85, 5]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print('Original DataFrame')
print(df)
print()
# pivot the dataframe
pivot_df = df.pivot(index='Date', columns='City')
print('Reshaped DataFrame')
print(pivot_df)输出
Original DataFrame
Date City Temperature Humidity
0 2023-01-01 New York 32 80
1 2023-01-01 Los Angeles 75 10
2 2023-01-02 New York 30 85
3 2023-01-02 Los Angeles 77 5
Reshaped DataFrame
Temperature Humidity
City Los Angeles New York Los Angeles New York
Date
2023-01-01 75 32 10 80
2023-01-02 77 30 5 85
在此示例中,我们为多个值即Temperature和Humidity创建了透视表。
pivot() vs pivot_table()
pivot()和pivot_table()函数执行类似的操作,但有一些关键区别。
| 依据 | pivot() | pivot_table() |
|---|---|---|
| 聚合 | 不允许数据聚合。 | 允许聚合(总和、平均值、计数等)。 |
| 重复索引 | 无法处理重复的索引值。 | 可以处理重复的索引值。 |
| 多级索引 | 仅接受单级索引。 | 接受多级索引以处理复杂数据。 |
