CSS的z-index属性用于控制已定位元素(positioned elements)的堆叠顺序。例如,
div.green {
position: absolute;
z-index: 3;
}
div.orange {
position: absolute;
z-index: 5;
}浏览器输出

在这里,z-index值较高的div堆叠在z-index值较低的div之上。
z-index属性仅对已定位元素和flex容器的子项生效。
position属性的值应不同于默认的static值。
CSS z-index 语法
z-index属性的语法如下:
z-index: auto | number | initial | inherit;这里,
auto:根据元素在HTML文档中的位置确定堆叠顺序(默认值)number:设置元素的堆叠顺序,允许负值initial:将属性值设置为默认值inherit:从父元素继承属性值
示例:CSS z-index 属性
让我们来看一个z-index属性的示例,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS z-index</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="greenyellow">position: absolute; <br />z-index: 3;</div>
<div class="orange">position: absolute; <br />z-index: 10;</div>
<div class="skyblue">position: absolute; <br />z-index: 6;</div>
</body>
</html>div {
font-size: 24px;
padding: 12px;
}
div.greenyellow {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
/* specifying z-index value */
z-index: 3;
width: 300px;
height: 280px;
background-color: greenyellow;
}
div.orange {
position: absolute;
top: 190px;
left: 0;
/* specifying z-index value */
z-index: 10;
width: 220px;
height: 150px;
margin-top: -120px;
background-color: orange;
}
div.skyblue {
position: absolute;
top: 120px;
left: 160px;
/* specifying z-index value */
z-index: 6;
width: 280px;
height: 150px;
padding-left: 120px;
background-color: skyblue;
}浏览器输出
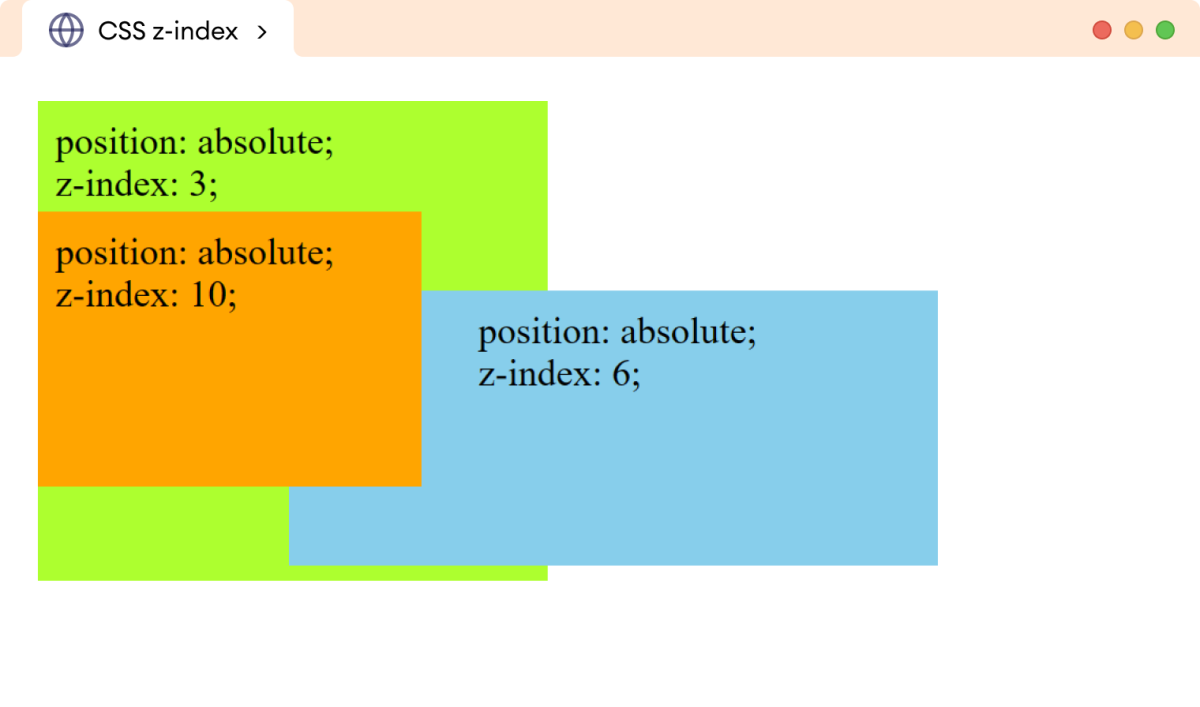
在上面的示例中,所有div元素的position值都为absolute。每个div元素还具有不同的z-index属性值。
z-index值较高的div堆叠在另一个div元素之上。
注意:具有相同z-index值的元素根据它们在HTML文档中的顺序进行堆叠。例如,如果元素B在元素A之后,那么元素A将堆叠在元素B之上。
CSS z-index 负值
具有负z-index值的元素会比具有正值的元素堆叠得更靠后。
让我们看一个例子,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS z-index</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="greenyellow">position: absolute; <br />z-index: 3;</div>
<div class="orange">position: absolute; <br />z-index: -4;</div>
</body>
</html>div {
font-size: 24px;
padding: 12px;
}
div.greenyellow {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
/* specifying z-index value */
z-index: 3;
width: 300px;
height: 150px;
background: greenyellow;
}
div.orange {
position: absolute;
top: 190px;
left: 0;
/* specifying negative z-index value */
z-index: -4;
width: 380px;
height: 80px;
margin-top: -120px;
padding-top: 120px;
background: orange;
}浏览器输出

在这里,z-index值为-4的div元素堆叠在z-index值为3的div元素之下。
带 Z-index 值的嵌套元素
z-index值在嵌套元素上的表现有所不同。
假设元素B堆叠在元素A之上,那么A的子元素永远无法堆叠在元素B之上。
我们来看一个例子,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<title>CSS z-index</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Creating a parent element having a child element -->
<div class="parent">
Parent Element<br />
position: relative; <br />z-index: 3;
<!-- Child elements have the highest z-index value -->
<div class="child">
Child Element <br />
z-index: 50;<br />
position: relative;
</div>
</div>
<div class="outer">
Outer Element <br />position: relative; <br />z-index: 6;
</div>
</body>
</html>div {
font-size: 24px;
padding: 12px;
}
div.parent {
position: relative;
top: 0;
left: 0;
/* specifying z-index value */
z-index: 3;
width: 500px;
height: 150px;
background: greenyellow;
}
div.child {
position: relative;
left: 200px;
top: -50px;
background: skyblue;
/* specifying negative z-index value */
z-index: 50;
width: 300px;
height: 120px;
padding-left: 120px;
}
div.outer {
position: relative;
top: -60px;
left: 0;
/* specifying negative z-index value */
z-index: 6;
width: 280px;
height: 120px;
background: orange;
}浏览器输出
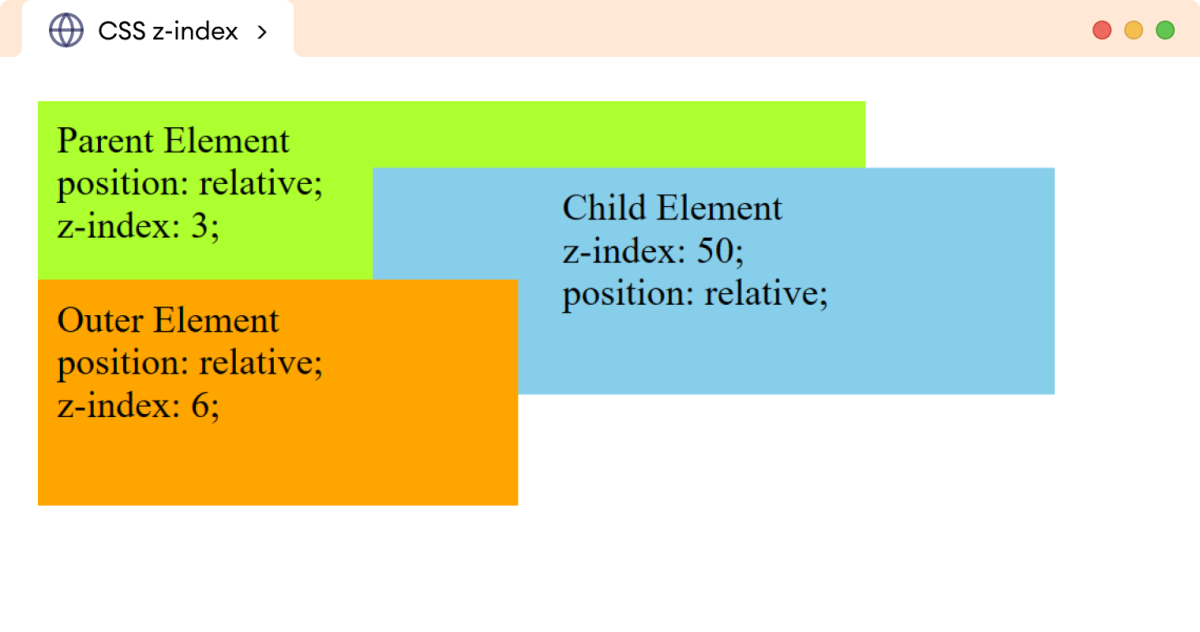
在上面的示例中,子div元素的z-index值为50,是最高的,但仍然堆叠在外层div元素的下方,其z-index值为6。
发生这种情况是因为外层div元素的z-index值高于其父元素。子元素不能堆叠在其父元素具有更高z-index值的元素之上。