match…case 语句允许我们根据表达式的值执行不同的操作。
Python 中 match...case 语句的语法是:
match expression:
case value1:
# code block 1
case value2:
# code block 2
...这里,expression 是要评估的值或条件。
如果 expression 等于
value1,则执行代码块 1。value2,则执行代码块 2。
在 match 语句中,只有一个选项会被执行。一旦找到匹配项,对应的代码块就会运行,其余的则会被跳过。
注意:match..case 语句是在 Python 3.10 中引入的,不适用于旧版本。它类似于其他编程语言(如 C++ 和 Java)中的 switch…case 语句。
现在,让我们看几个 match..case 语句的例子。
示例 1:Python match...case 语句
operator = input("Enter an operator: ")
x = 5
y = 10
match operator:
case '+':
result = x + y
case '-':
result = x - y
case '*':
result = x * y
case '/':
result = x / y
print(result)输出 1
Enter an operator: * 50
operator 变量存储用户输入,表示一个数学运算符。match 语句评估 operator 的值并运行相应的代码块。
如果 operator 是
+: 执行result = x + y。-: 执行result = x - y。*: 执行result = x * y。/: 执行result = x / y。
虽然此程序适用于输入 +、-、* 和 /,但如果我们输入任何其他字符作为运算符,则会导致错误。
输出 2
Enter an operator: % ERROR! NameError: name 'result' is not defined
我们收到此错误是因为输入值(%)与任何 case 都不匹配。
为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用默认情况。
默认情况
我们使用默认情况,如果所有 case 都不匹配,则执行默认情况。下面是默认情况的使用方法:
match expression:
case value1:
....
case value2:
...
case _: # default case
....这里,_ 代表默认情况。
让我们使用默认情况解决上面的错误。
示例 2:默认情况
operator = input("Enter an operator: ")
x = 5
y = 10
match operator:
case '+':
result = x + y
case '-':
result = x - y
case '*':
result = x * y
case '/':
result = x / y
case _:
result = "Unsupported operator"
print(result)输出
Enter an operator: % Unsupported operator
用流程图理解 Python match...case
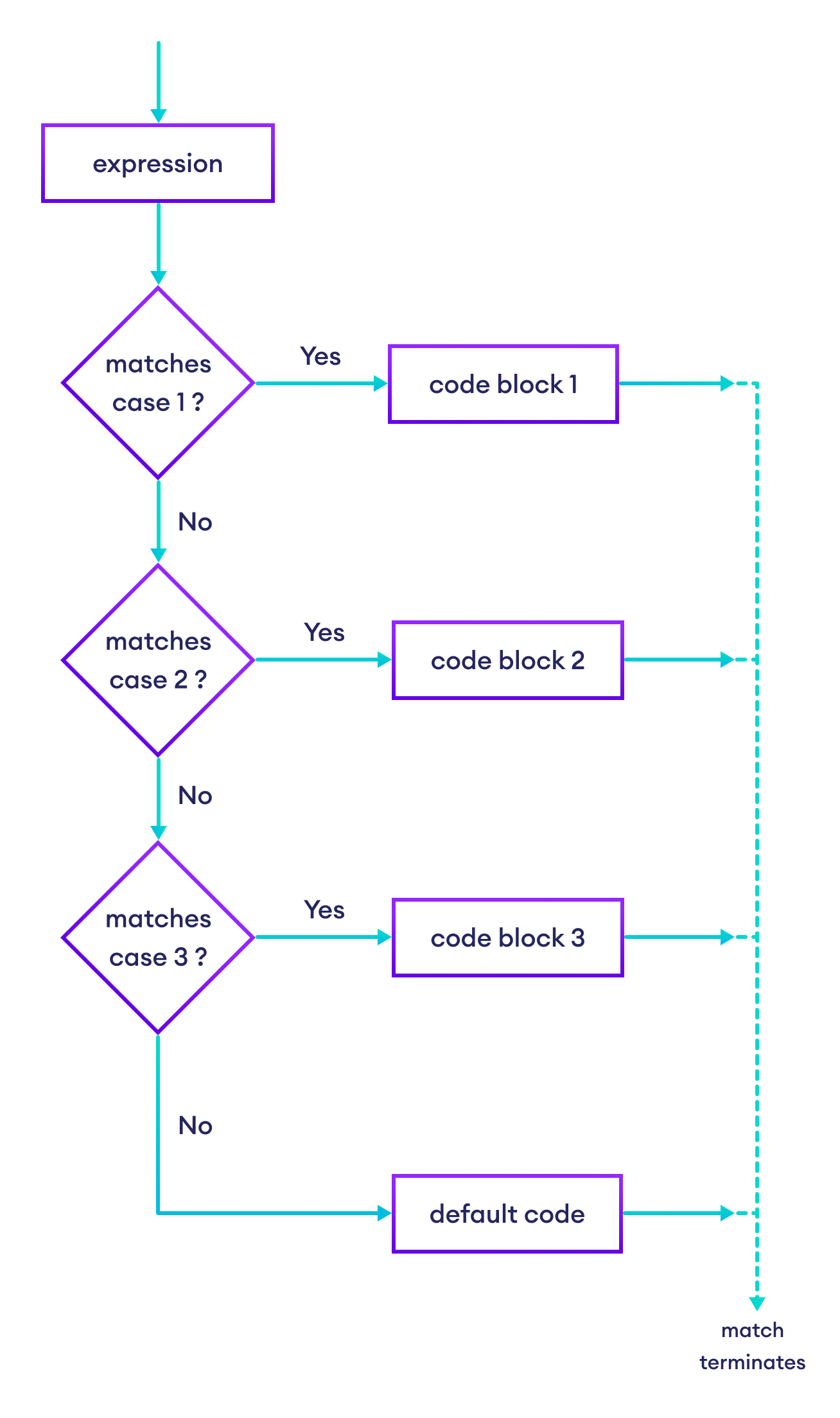
使用 match...case 与 | 运算符
Python 中的 match...case 语句非常灵活。例如,可以使用 | 运算符在 case 子句中将表达式与多个值进行匹配。
例如,
status = int(input("Enter the status code: "))
match status:
case 200 | 201 | 202:
print("Success")
case 400 | 401 | 403:
print("Client error")
case 500 | 501 | 502:
print("Server error")
case _:
print("Unknown status")输出 1
Enter the status code: 500 Server error
输出 2
Enter the status code: 700 Unknown status
在每个 case 中,| 运算符用于匹配多个值。如果 status 值与某个 case 中的任何值匹配,则执行该 case 中的代码。
200 | 201 | 202: 如果状态为 200、201 或 202,则打印"成功"。400 | 401 | 403: 如果状态为 400、401 或 403,则打印"客户端错误"。500 | 501 | 502: 如果状态为 500、501 或 502,则打印"服务器错误"。
在 Case 中使用 Python if 语句
在 Python 中,我们还可以在 case 子句中使用 if 语句。这称为守卫,它为表达式添加了一个额外的条件。
如果守卫条件(if 语句)评估为 False,则 match 语句会跳过该 case 并继续到下一个。
例如,
subject = input("Enter a subject: ")
score = int(input("Enter a score: "))
match subject:
# if score is 80 or higher in Physics or Chemistry
case 'Physics' | 'Chemistry' if score >= 80:
print("Excellent in Science!")
# if score is 80 or higher in English or Grammar
case 'English' | 'Grammar' if score >= 80:
print("Excellent in English!")
# if score is 80 or higher in Maths
case 'Maths' if score >= 80:
print("Excellent in Maths!")
case _:
print(f"Needs improvement in {subject}!")输出 1
Enter a subject: Chemistry Enter a score: 95 Excellent in Science!
这里,执行了 case 'Physics' | 'Chemistry' if score >= 80:,因为 subject 匹配 "Chemistry",并且 score 95 满足 if 条件(score >= 80)。
在 case 子句中,我们使用 if 语句添加了一个额外的条件。这里,它检查 score 是否为 80 或更高。
注意:当我们在 case 中使用 if 语句时,if 条件仅在找到 case 匹配后才进行评估。
